Intro
Dkron - Distributed, fault tolerant job scheduling system
Welcome to the Dkron documentation! This is the reference guide on how to use Dkron. If you want a getting started guide refer to the getting started guide.
What is Dkron
Dkron is a distributed system to run scheduled jobs against a server or a group of servers of any size. One of the machines is the leader and the others will be followers. If the leader fails or becomes unreachable, any other one will take over and reschedule all jobs to keep the system healthy.
In case the old leader becomes alive again, it'll become a follower.
Dkron is a distributed cron drop-in replacement, easy to setup and fault tolerant with focus in:
- Easy: Easy to use with a great UI
- Reliable: Completely fault tolerant
- Highly scalable: Able to handle high volumes of scheduled jobs and thousands of nodes
Dkron is written in Go and leverages the power of distributed key value stores and Serf for providing fault tolerance, reliability and scalability while remaining simple and easily installable.
Dkron is inspired by the google whitepaper Reliable Cron across the Planet
Dkron runs on Linux, OSX and Windows. It can be used to run scheduled commands on a server cluster using any combination of servers for each job. It has no single points of failure due to the use of the fault tolerant distributed databases and can work at large scale thanks to the efficient and lightweight gossip protocol.
Dkron uses the efficient and lightweight gossip protocol underneath to communicate with nodes. Failure notification and task handling are run efficiently across an entire cluster of any size.
For a detailed overview of Dkron's internal architecture, components, and how they work together, see the Architecture documentation.
Key Concepts
Jobs
Jobs are the core entity in Dkron. A job consists of:
- Name: Unique identifier for the job
- Schedule: When to run the job (cron expression)
- Command: What to run
- Executor: How to run the command (shell, HTTP, etc.)
- Processors: How to process the output
- Tags: Key-value pairs for node selection
- Concurrency: Options to control concurrent execution
- Dependent Jobs: Jobs that should run after this job completes
Tags and Node Selection
Dkron uses tags to control which nodes execute specific jobs:
- Node Tags: Assigned to nodes during startup (
--tag key=value) - Job Tags: Specified in job definitions (
"tags": {"role": "web"}) - Tag Matching: Jobs run on nodes where all job tags match node tags
Concurrency Options
Dkron provides several options to control job concurrency:
- Concurrency: Allow (or disallow) concurrent executions of the same job
Status Codes and Retries
Jobs can be configured with:
- Retries: Number of times to retry a failed execution
Job Dependencies
Dkron supports job dependencies for complex workflows:
- Parent-Child Relationships: Jobs can depend on other jobs
- Status Checking: Child jobs run only if parent jobs succeed
- Chained Execution: Create multi-step job pipelines
Web UI
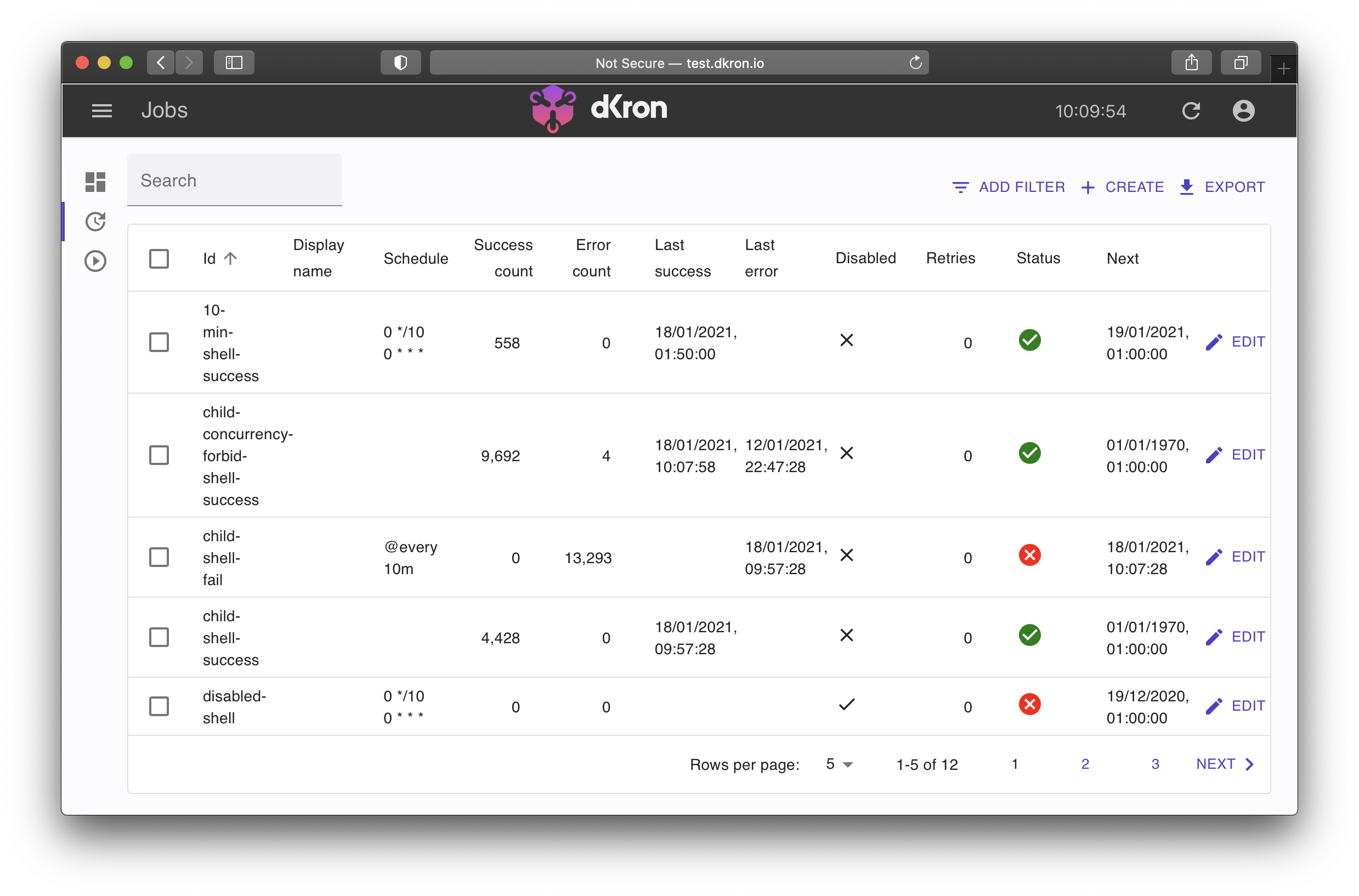
The Dkron web UI provides an easy-to-use interface for:
- Creating and editing jobs
- Viewing execution history and logs
- Monitoring cluster status
- Running jobs manually
- Managing job dependencies
Design Philosophy
Dkron is designed to solve one problem well: executing commands at given intervals. Following the Unix philosophy of doing one thing and doing it well (like the battle-tested cron), but with the addition of being designed for the cloud era, removing single points of failure in environments where scheduled jobs need to be run across multiple servers.